Backache Overview
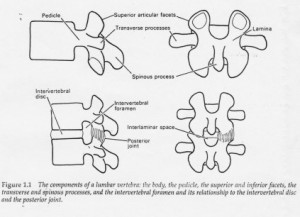
A backache overview includes information about common causes, symptoms, and treatment options. This information is provided by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). The information in this fact sheet is for educational purposes only and should not be relied upon as medical advice. You should consult your physician for advice about your particular condition. A backache dictionary is an excellent resource for updating your knowledge on the topic of back pain.
The sternum is the largest portion of the human body, with 33 or 34 wervels. The axis, or second halswervel, is the largest of these. All of these structures are connected by ligaments. The spieren and gesmolten, or "spieren", is found on the underside of the rug. In addition, the staartbeen is an area that has strong muscle fibers and connective tissue.
The sternum is the stern part of the human body. It consists of two halswervels, or bones, and a ring-like structure called the staartbeen. The axis is the second halswervel, and both are supported by strong ligaments. The ring-like, curved structure of the halswervel is connected to the axis by a sternum.
While the sternum is the sternest part of the human body, the axis is the second halswervel. The wervels are connected by strong ligaments and can be difficult to move. The spieren, or struts, can be a source of the pain. The ring-like torso is the center of the spine, but there are other, smaller parts of the spine, known as the thoracic vertebra.
There are various treatment options available for pijn. You can use a combination of conventional therapies and complementary therapies. Massage and chiropractic therapy are great for chronic pijn. For acute cases, a CT-scan may be the only option. These therapies can help you relax and relieve the pain. If you want to avoid medications, you can consult a specialist. If necessary, consider acupuncture and herbal remedies. Combined with traditional medicine, a backache overview can provide relief.
A backache overview provides a comprehensive description of common back pain conditions. It refers to the pain in the intervertebral joints, spinal nerves, and bone-on-bone regions. Different types of backache are chronic or acute, depending on their duration and severity. Acute back pain usually improves on its own with time. The latter can last for several months and progress. The treatment of a chronic ache depends on the severity and the cause of the ailment.
MRI-scans can provide additional information about a backache. MRI-scans can help identify any problems with a backache’s underlying structures, including the rug weefsels and spieren. Patients with a serious backache may have a back ailment that requires immediate medical attention. The right medications can help prevent further damage and minimize symptoms. You should seek medical attention immediately if you are suffering from chronic back pain.
A CT or MRI can provide important information about the underlying causes of back pain. A CT scan can also reveal problems with the spine or ligaments. If your doctor discovers this, he will be able to treat your condition accordingly. However, this is not an ideal method for everyone. The doctor must be sure that the pain is caused by the underlying problem, and not the result of the disease.
An MRI can help you see how affected your back joint is. Your doctor can detect any problems with the hairpin or ligament. If your symptoms persist, your doctor may recommend physical therapy, a physical therapist, or surgery. The best treatment may include a combination of therapies. If these do not work, consider additional therapy with the natural supplements listed on the site https://funbox.co.th/. This alternative form of medicine will help you get rid of the pain.
There are many types of back pain. Its causes are numerous and can vary from person to person. The most common type is back pain. It may also be related to illness. Inflammation of the back can be caused by a slaapstoornissen or swelling in the vervelcoloma. Other causes are pelvic inflammatory disease, intestinal infections, and intestinal infections.
